5 Easy-to-miss signs of vitamin D deficiency: Are YOU getting enough?
10/30/2017 / By Janine Acero
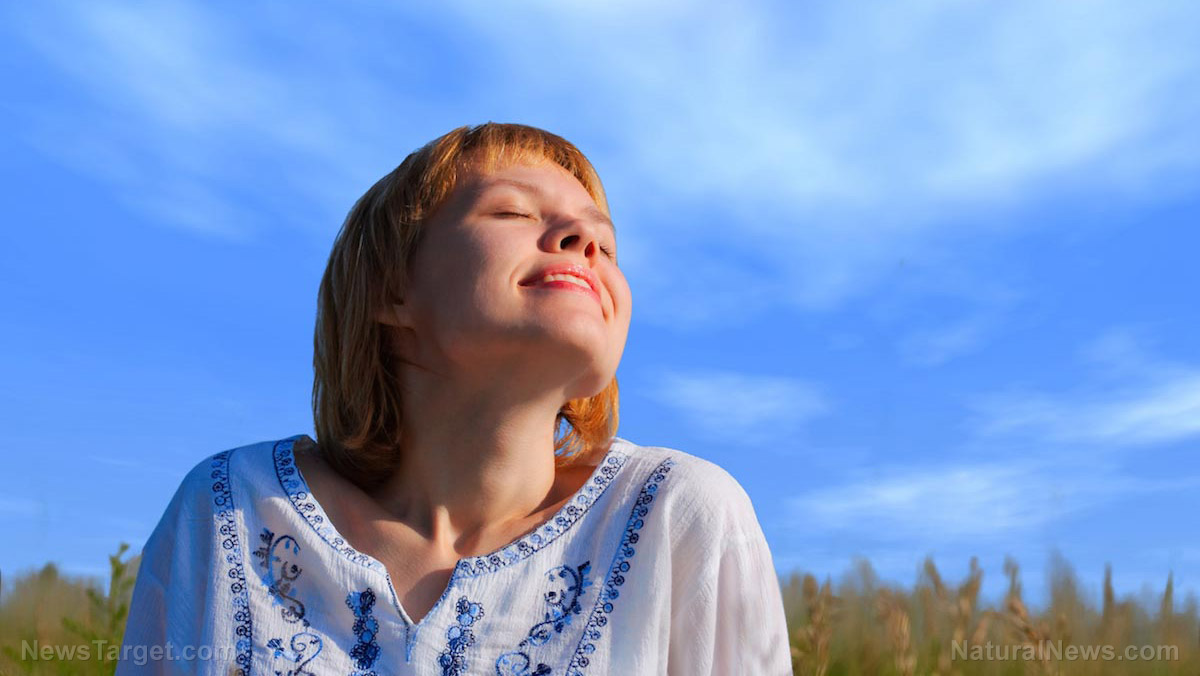

Vitamin D is a nutrient that your body produces when your skin absorbs sunlight, earning the nickname “sunshine vitamin.” Despite the name however, vitamin D is technically a pro-hormone, and not a vitamin. Your body cannot create vitamins by itself, therefore you need to rely on food and supplement for your vitamin intake. However, your body can synthesize vitamin D when your skin absorbs sunlight.
Inadequate levels of vitamin D can cause many health problems such as infections and muscle pains, but dangerously deficient people may develop cardiovascular diseases and even cancer, in particular the colorectal, breast, pancreatic and prostate varieties.
Here are some of the more common signs of vitamin D deficiency:
- Frequent infections – Vitamin D is vital to the immune system. Insufficient amounts will impair the ability of the immune cells to react to infections. “Vitamin D is essential to the function of two essential parts of the immune system, adaptive and innate immunity,” said nutritionist Kim Pearson. Adaptive immunity remembers the viruses that have once entered your body (like chicken pox) and prevents them from coming back, while your innate immunity protects you from everyday infections like colds.
- Feeling depressed – Vitamin D deficiency can affect mood, especially during winter. A 2014 study found a direct link between vitamin D and Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD)
which triggers low mood during winter months because of lack of sunshine. - Always feeling tired – Vitamin D is essential to for converting food into energy. Your body’s ability to assimilate nutrients from your food is compromised by the lack of vitamin D, but this can be remedied by supplementation.
- Weak bones and joint pains – A 2014 study predicted that people older than 50 are more likely to develop hip and knee joint pains with low levels of vitamin D. “When you’re running low on vitamin D, your bones can weaken increasing your risk of stress fractures,” said Pearson.
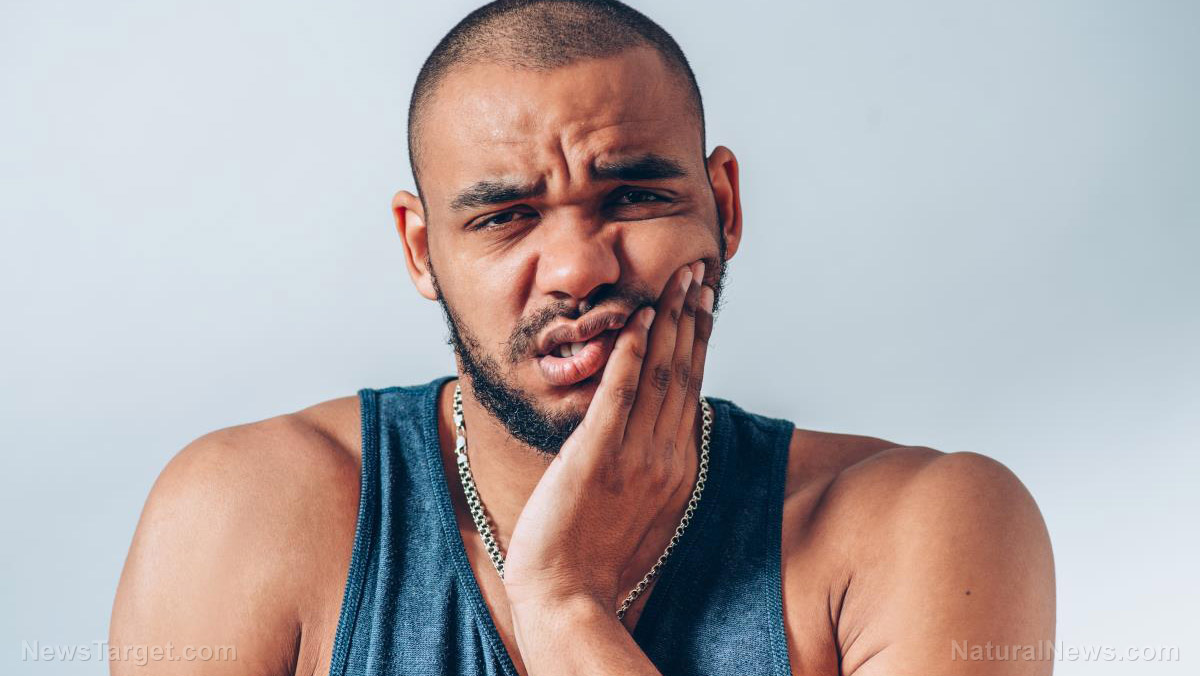
- Muscle pain – Vitamin D supports muscle function and muscle strength when metabolized by the body. “Having lots of general muscle aches is often the first tell tale sign of a deficiency,” Pearson cautioned.
Not enough exposure to sunlight will deplete your levels of vitamin D. Common everyday discomfort like recurring colds to aches and pains may result from a vitamin D deficiency, which gives you enough excuse to go outdoors and soak up some sun.
However, thanks to modern urban lifestyles, we’re seeing an increasing number of people who are vitamin D deficient. From children choosing their mobile devices and video games over outdoor activities, to busy employees spending most of the day cooped up inside office buildings, more people are spending their time indoors. Current estimates have a staggering one in five adults and one in six children having inadequate levels of vitamin D.
Pearson explained that people with darker skin types have the most difficulty synthesizing vitamin D which makes them more susceptible to deficiency. Others at risk include pregnant and breastfeeding women and those who cover their skin for religious purposes.
“I regularly test my client’s vitamin D levels and of the last 20 clients that I have tested, six were deficient, six had suboptimal levels and just eight had optimal levels,” said Pearson. “Those with optimal levels were usually either supplementing, or spent a significant amount of time abroad in sunnier places.”
How to get your vitamin D
The best way to get your vitamin D is to go outdoors and expose your skin (without sunscreen) under the sun for about 20 minutes. People with darker skin types will have to spend more time soaking up the rays to produce the same amount of vitamin D.
You can likewise get your vitamin D in foods such as fish oil (cod liver oil) and fatty fish (herring, sockeye salmon, sardines and tuna). You may also want to stock up on supplements and vitamin oral sprays. (Related: The best dietary sources of vitamin D.)
Read more about vitamin deficiency at SupplementsReport.com.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: dietary supplements, disease prevention, nutrition, supplements, vitamin D, vitamin deficiency