Used for thousands of years in TCM, Psoralea corylifolia treats a variety of diseases from heart disease to cancer
10/08/2019 / By Evangelyn Rodriguez

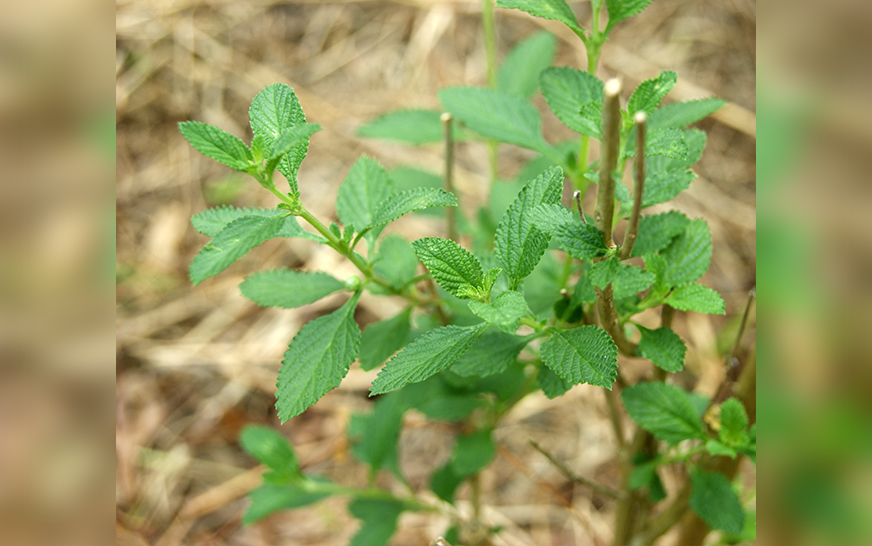
Psoralea corylifolia or babchi is a medicinal herb that is popular among traditional Chinese medicine and Ayurveda practitioners. It is used to treat various skin diseases, including rashes, psoriasis, leprosy, and leucoderma – a condition that causes the appearance of white patches due to loss of melanin. However, several studies have reported that P. corylifolia has other clinical applications, and these can be attributed to its abundance in bioactive components. In a review published in The American Journal of Chinese Medicine, researchers from the University of Macau systematically summarized studies on the chemical constituents and biological activities of P. corylifolia. In it, they discuss the efficacy of P. corylifolia in treating a variety of diseases, ranging from cardiovascular diseases and bone diseases to cancer.
Psoralea corylifolia is rich in phytochemicals that exhibit different biological activities
Indigenous herbs have long been used as remedies in traditional medicinal practices. They are relatively safe, easily available, and cause fewer to no adverse effects compared with modern treatments. For these reasons, many patients are beginning to rely on natural medicines as adjunct treatments, and researchers are continuing to investigate these herbs’ therapeutic potential. (Related: Bu Gu Zhi: The Scruffy Pea Contains Amazing Tonic and Healing Power.)
P. corylifolia is an important medicinal plant that has been used for thousands of years. It is a small, erect, perennial herb that is widely distributed in tropical and subtropical regions, such as in China, India, and South Africa. One of the best things about P. corylifolia is that every part of it — roots, leaves, seeds, and blooms — can be used. The dried fruit of P. corylifolia is considered a popular traditional Chinese medicine, and it is officially listed in the Chinese Pharmacopoeia.
The different parts of P. corylifolia can be used for the following:
- Blooms – either in powder form or as a paste or ointment, can treat leucoderma and leprosy
- Oil – has a powerful effect on Streptococci (bacteria) and can alleviate inflammatory conditions, such as mucous membrane disorders, dermatitis, boils, and skin eruptions. It also has blood-purifying properties.
- Seeds – can cure scorpion stings and snakebites. They can also treat bilious disorders, bacterial infections, asthma, cough, and nephritis. Seed extracts and powder can be used as a diuretic, anthelminthic, laxative, vulnerary (wound healing), stimulant, aphrodisiac, and diaphoretic (induces perspiration). They can also be used to treat alopecia and prevent hair loss.
- Roots – can treat teeth caries and other dental problems; protects against osteoporosis and bone fractures. They also promote bone calcification
- Fruits – help prevent vomiting, improve the complexion, and treat difficulty in micturition (urinating), piles, bronchitis, and anemia
- Leaves – can be used to alleviate diarrhea
According to studies conducted on the phytochemical components of P. corylifolia, its main active components are coumarins, flavonoids, and meroterpenes. Most of these components are present in the seeds or fruits of P. corylifolia. Some of the notable phytochemicals present in these parts are:
- Bavachinin A – flavonoid found in the fruits of P. corylifolia; exhibits anti-inflammatory, antipyretic, and mild analgesic activities.
- Corylifolinin – flavonoid isolated from benzene seed extracts; can cause coronary vasodilation and inhibit the growth and proliferation of cancer cells; has estrogenic effects.
- Bakuchiol – meroterpene found in seeds; has antibacterial, antioxidant, and hepatoprotective properties.
- Psoralidin – furanocoumarin present in P. corylifolia seeds; has a cytotoxic effect on stomach cancer cells; also exhibits anti-tumor activity.
- Psoralen and isopsoralen – furanocoumarins found in P. corylifolia seeds; have anti-tumor, antibacterial, and antiviral properties.
P. corylifolia is an herb with a lot of therapeutic value. It is also a good source of phytochemicals that can be used to treat several diseases. The researchers believe that their review provides useful information that could help future researchers evaluate and prove the potency and clinical applications of this medicinal plant.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: alternative medicine, anti-inflammatory, anticancer, antidepressant, Antimicrobial, antioxidant, antitumor, babchi, bakuchiol, bavachinin A, bone disease, bone health, cancer, cancer cures, cancer treatment, cardiovascular disease, clean food, corylifolinin, coumarins, disease treatments, flavonoids, food cures, food is medicine, food safety, functional food, furanocoumarins, heart health, hepatoprotective, herbal medicine, Herbs, isopsoralen, meroterpenes, natural cures, natural medicine, phytonutrients, Psoralea corylifolia Linn, psoralen, psoralidin, research, skin disease, skin health, TCM, traditional Chinese medicine
RECENT NEWS & ARTICLES
COPYRIGHT © 2017 PREVENT CANCER NEWS